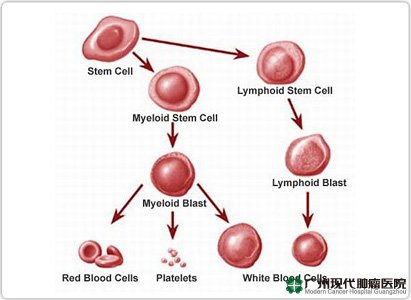
Leukemia is a type of disorder of the hematopoietic stem cell system of creation which is also a disease that is quite fierce. Abnormalities of the ability to further differentiation and maturation of leukocytes stagnant at different stages of cell development in the bone marrow and other hematopoietic tissues. Figures accumulation of abnormal cells and the infiltration of other organs and tissue, and normal hematopoietic function suppression. Leukemia commonly cause anemia, bleeding infection, and symptoms of organ infiltration.
How high rates of leukemia?
Leukemia or blood cancer anka occupy 2.5% of the total cancer existing cancer. Around the world, every year there are about 47,150 people who are diagnosed as suffering from leukemia. And every year anyway, there are about 23,540 people who died of leukemia cases. In childhood cancer, usually leukemia risk will be high at the age of 0-4 years, and in men and women comparison rate is 7: 5.

Types of leukemia are the most common?
Based on morphological characteristics and cell source, leukemia can be divided into categories - categories as follows:
Acute myeloid 1.leukemia: a type of white blood cell proliferation of abnormal myeloid leukemia. Acute myeloid leukemia is characterized by the rapid proliferation of abnormal cells in the bone marrow and affect the growth of normal blood cells other.
Chronic myeloid 2.Leukemia: ie clones disease in hematopoietic stem cell proliferation, which also has a proliferation of bone marrow, blood leukocytosis generally will multiply and have an enlarged spleen, symptoms of which is the main feature of chronic myeloid leukemia.
Acute lymphoblastic 3.Leukemia: is a disruption in lymphoblastoid cell hyperplasia and abnormalities in lymphoblastoid cell formation or differentiation of large numbers of mature white blood cells in the block, which is a leukemia that can develop rapidly.
Chronic lymphocytic 4.Leukemia: This type of leukemia is a malignant tumor that affects lymphocytes, chronic lymphocytic leukemia characterized by a large number of immature lymphocytes cell aggregation, inhibit normal hematopoietic bone marrow.
What causes leukemia?
Although many factors are suspected to be the cause of leukemia, but the cause of leukemia is not yet fully ascertained. The cause of leukemia is generally due to infection, radiation factors, chemical factors and genetic factors.
What are the symptoms of leukemia?
1.Anemia: that seems clear is colored pale face, dizziness, palpitations, etc. ...
2.Demam: fever or heat that sometimes arise sometimes improved, body temperature is usually around 37.5 to 40 ℃ or even higher.
3.Pendarahan: bleeding are common in some parts of the body, such as the nasal cavity, oral cavity, gums, and other parts.
4.Kelenjar nodes: enlarged lymph nodes throughout the body, more commonly encountered in patients with acute lymphoblastic leukemia.
5.Pembesaran liver and spleen: 50% of leukemia patients generally have an enlarged liver and spleen, but is most often found in patients with acute lymphoblastic leukemia.
6.Infeksi nervous system: arachnoid, meninges (lining of the brain) etc. infiltration of leukocytes, resulting in increased intracranial pressure and limb paralysis.
Her other 7.Gejala: When the cancer cell infiltration into other parts of the respiratory, digestive, and urogenital systems will be affected by pleural effusion, and symptoms of gastrointestinal dysfunction and proteinuria.
What causes leukemia?
Although many factors are suspected to be the cause of leukemia, but the cause of leukemia is not yet fully ascertained. The cause of leukemia is generally due to infection, radiation factors, chemical factors and genetic factors.
What are the symptoms of leukemia?
1.Anemia: that seems clear is colored pale face, dizziness, palpitations, etc. ...
2.Demam: fever or heat that sometimes arise sometimes improved, body temperature is usually around 37.5 to 40 ℃ or even higher.
3.Pendarahan: bleeding are common in some parts of the body, such as the nasal cavity, oral cavity, gums, and other parts.
4.Kelenjar nodes: enlarged lymph nodes throughout the body, more commonly encountered in patients with acute lymphoblastic leukemia.
5.Pembesaran liver and spleen: 50% of leukemia patients generally have an enlarged liver and spleen, but is most often found in patients with acute lymphoblastic leukemia.
6.Infeksi nervous system: arachnoid, meninges (lining of the brain) etc. infiltration of leukocytes, resulting in increased intracranial pressure and limb paralysis.
Her other 7.Gejala: When the cancer cell infiltration into other parts of the respiratory, digestive, and urogenital systems will be affected by pleural effusion, and symptoms of gastrointestinal dysfunction and proteinuria.


 12:32 AM
12:32 AM
 admin
admin

 Posted in:
Posted in: 




0 comments:
Post a Comment